1 | /* |
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x13) - 串口UART驱动API
串口驱动API ## 1、uart_register_driver
1 | /* 功能: uart_register_driver用于将串口驱动uart_driver注册到内核(串口核心层)中,通常在模块初始化函数调用该函数。 |
1 | /* 功能: uart_unregister_driver用于注销我们已注册的uart_driver,通常在模块卸载函数调用该函数 |
3、uart_add_one_port
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x12) - uart_ops结构体
1 | /* |
set_mctrl(port, mctrl)
此函数设置串口modem控制模式。mctrl相关的位是: - TIOCM_RTS RTS signal. - TIOCM_DTR DTR signal. - TIOCM_OUT1 OUT1 signal. - TIOCM_OUT2 OUT2 signal. - TIOCM_LOOP 设置端口为回环模式
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x11) - uart_port结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70struct uart_port {
spinlock_t lock; /* 串口端口锁 */
unsigned int iobase; /* IO端口基地址 */
unsigned char __iomem *membase; /* IO内存基地址,经映射(如ioremap)后的IO内存虚拟基地址 */
unsigned int irq; /* 中断号 */
unsigned int uartclk; /* 串口时钟 */
unsigned int fifosize; /* 串口FIFO缓冲大小 */
unsigned char x_char; /* xon/xoff字符 */
unsigned char regshift; /* 寄存器位移 */
unsigned char iotype; /* IO访问方式 */
unsigned char unused1;
#define UPIO_PORT (0) /* IO端口 */
#define UPIO_HUB6 (1)
#define UPIO_MEM (2) /* IO内存 */
#define UPIO_MEM32 (3)
#define UPIO_AU (4) /* Au1x00 type IO */
#define UPIO_TSI (5) /* Tsi108/109 type IO */
#define UPIO_DWAPB (6) /* DesignWare APB UART */
#define UPIO_RM9000 (7) /* RM9000 type IO */
unsigned int read_status_mask; /* 关心的Rx error status */
unsigned int ignore_status_mask;/* 忽略的Rx error status */
struct uart_info *info; /* pointer to parent info */
struct uart_icount icount; /* 计数器 */
struct console *cons; /* console结构体 */
#ifdef CONFIG_SERIAL_CORE_CONSOLE
unsigned long sysrq; /* sysrq timeout */
#endif
upf_t flags;
#define UPF_FOURPORT ((__force upf_t) (1 << 1))
#define UPF_SAK ((__force upf_t) (1 << 2))
#define UPF_SPD_MASK ((__force upf_t) (0x1030))
#define UPF_SPD_HI ((__force upf_t) (0x0010))
#define UPF_SPD_VHI ((__force upf_t) (0x0020))
#define UPF_SPD_CUST ((__force upf_t) (0x0030))
#define UPF_SPD_SHI ((__force upf_t) (0x1000))
#define UPF_SPD_WARP ((__force upf_t) (0x1010))
#define UPF_SKIP_TEST ((__force upf_t) (1 << 6))
#define UPF_AUTO_IRQ ((__force upf_t) (1 << 7))
#define UPF_HARDPPS_CD ((__force upf_t) (1 << 11))
#define UPF_LOW_LATENCY ((__force upf_t) (1 << 13))
#define UPF_BUGGY_UART ((__force upf_t) (1 << 14))
#define UPF_MAGIC_MULTIPLIER ((__force upf_t) (1 << 16))
#define UPF_CONS_FLOW ((__force upf_t) (1 << 23))
#define UPF_SHARE_IRQ ((__force upf_t) (1 << 24))
#define UPF_BOOT_AUTOCONF ((__force upf_t) (1 << 28))
#define UPF_FIXED_PORT ((__force upf_t) (1 << 29))
#define UPF_DEAD ((__force upf_t) (1 << 30))
#define UPF_IOREMAP ((__force upf_t) (1 << 31))
#define UPF_CHANGE_MASK ((__force upf_t) (0x17fff))
#define UPF_USR_MASK ((__force upf_t) (UPF_SPD_MASK|UPF_LOW_LATENCY))
unsigned int mctrl; /* 当前的moden设置 */
unsigned int timeout; /* character-based timeout */
unsigned int type; /* 端口类型 */
const struct uart_ops *ops; /* 串口端口操作函数集 */
unsigned int custom_divisor;
unsigned int line; /* 端口索引 uart_driver.dev_name加上line组成串口的设备节点的名字 */
resource_size_t mapbase; /* IO内存物理基地址,可用于ioremap */
struct device *dev; /* 父设备 */
unsigned char hub6; /* this should be in the 8250 driver */
unsigned char suspended;
unsigned char unused[2];
void *private_data; /* 端口私有数据,一般为platform数据指针 */
};
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x10) - uart_driver结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16struct uart_driver {
struct module *owner; /* 拥有该uart_driver的模块,一般为THIS_MODULE */
const char *driver_name; /* 串口驱动名,串口设备文件名以驱动名为基础 */
const char *dev_name; /* 串口设备名 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
int minor; /* 次设备号 */
int nr; /* 该uart_driver支持的串口个数(最大) */
struct console *cons; /* 其对应的console.若该uart_driver支持serial console,否则为NULL */
/*
* these are private; the low level driver should not
* touch these; they should be initialised to NULL
*/
struct uart_state *state;
struct tty_driver *tty_driver;
};
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x0F) - Cannot access memory at address
按照教程Linux内核调试环境搭建(基于ubuntu12.04) 配置kgdb双机调试时,出现一下错误:
1 | (gdb) set serial baud 115200 |
解决方法是:在grub.cfg中添加rodata=off nokaslr
也就是在
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x0E) - vm_area_struct结构体
内存映射信息放在vma参数中,注意,这里的vma的数据类型是struct vm_area_struct,它表示的是一块连续的虚拟地址空间区域,在函数变量声明的地方,我们还看到有一个类似的结构体struct vm_struct,这个数据结构也是表示一块连续的虚拟地址空间区域。
那么,这两者的区别是什么呢?在Linux中,struct vm_area_struct表示的虚拟地址是给进程使用的,而struct vm_struct表示的虚拟地址是给内核使用的,它们对应的物理页面都可以是不连续的。struct vm_area_struct表示的地址空间范围是0~3G,而struct vm_struct表示的地址空间范围是(3G + 896M + 8M) ~ 4G。struct vm_struct表示的地址空间范围为什么不是3G~4G呢?原来,3G ~ (3G + 896M)范围的地址是用来映射连续的物理页面的,这个范围的虚拟地址和对应的实际物理地址有着简单的对应关系,即对应0~896M的物理地址空间,而(3G + 896M) ~ (3G + 896M + 8M)是安全保护区域(例如,所有指向这8M地址空间的指针都是非法的),因此struct vm_struct使用(3G + 896M + 8M) ~ 4G地址空间来映射非连续的物理页面。
1 | /* |
linux内核使用vm_area_struct结构来表示一个独立的虚拟内存区域,由于每个不同质的虚拟内存区域功能和内部机制都不同,因此一个进程使用多个vm_area_struct结构来分别表示不同类型的虚拟内存区域。各个vm_area_struct结构使用链表或者树形结构链接,方便进程快速访问,如下图所示:
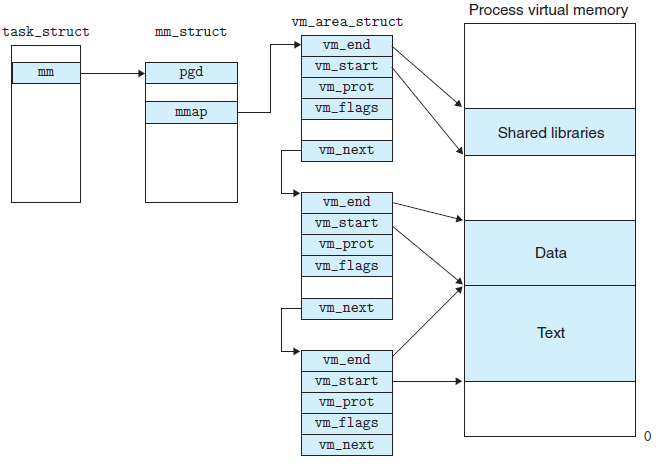
vm_area_struct结构中包含区域起始和终止地址以及其他相关信息,同时也包含一个vm_ops指针,其内部可引出所有针对这个区域可以使用的系统调用函数。这样,进程对某一虚拟内存区域的任何操作需要用要的信息,都可以从vm_area_struct中获得。mmap函数就是要创建一个新的vm_area_struct结构,并将其与文件的物理磁盘地址相连。
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x0D) - remap_pfn_range()
驱动实现mmap主要是调用:
1 | int remap_pfn_range(struct vm_area_struct *, unsigned long addr, |
函数来映射,声明在include/linux/mm.h。 第一个参数:虚拟地址描述结构体(声明在include/linux/mm_types.h,起始mm.h中已经包含了它),一般是系统传递下来。 第二个参数:虚拟起始地址 第三个参数:物理地址 第四个参数:映射空间大小,单位字节 第五个参数:给新 VMA 要求的”protection”. 驱动直接使用 vma->vm_page_prot
返回值,成功返回0,否则返回-1;
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x0C) - SetPageReserved()
SetPageReserved()
随着linux的长时间运行,空闲页面会越来越少,为了防止linux内核进入请求页面的僵局中,Linux内核采用页面回收算法(PFRA)从用户进程和内核高速缓存中回收内存页框,并根据需要把要回收页框的内容交换到磁盘上的交换区。调用该函数可以使页面不被交换。
1
#define SetPageReserved(page) set_bit(PG_reserved,&(page)->flags)
Linux驱动开发杂记(0x0B) - 内核计数
.h**
1 | /* |
.11.c
1 | #include <linux/kref.h> |